Glossary
There’s nothing more that a marketer (even more so – a digital marketer) likes than jargon, acronyms and general hoodwinkery. Not us though – we’re constantly working hard to simplify the complex, lift the veil, and like a really bad magician – give away our secrets.
So to help keep things simple, and make it easier for you to understand what we’re talking about, we’ve put together simple, no-nonsense explanations of key marketing terms. Looking for a word, but it’s not in here? Flick us an email at hello@rogerroger.marketing and we’ll make sure to add it.
A
AB Testing
A/B Testing is the process of taking a marketing asset and creating two versions, with only one difference, to test which is more effective. By splitting your audience in half, we can compare the results of each and use these insights to make sure future marketing is on point.
Marketing asset examples:
- Email marketing campaigns
- Websites
- Applications
- Digital advertising
- Landing pages
- E-Newsletters
Variable examples:
- Fonts
- Colour
- Layout
- Heading or subject line text
- Call to action
- Image
- Pricing
- Special offers
Benefits:
- Allows agility in your campaigns
- Higher click-through and conversion rates
- Gain a greater understanding of your target audience
- Lower bounce rates (people leaving quickly)
- Low cost to conduct with possible high return
Similar Terms:
- Split Testing
- Bucket Testing
Audience Segmentation
Audience Segmentation is the process of dividing your audience into smaller groups based on things they have in common. Once your audience is split into relevant groups you can send them more personal messaging. We don’t speak to every customer the same way in person, so why do it in digital marketing?
Segment Examples:
Separating your audience into smaller groups requires choosing the criteria of which you will use to segment. Examples below:
- Behaviour – purchasing style, engagement, preferred type of communication
- Demographic – age, gender, family circumstance
- Location – Place of work, Place or living
- Attitude – Personal interests, values, lifestyle choices/li>
Benefits:
- More love from your customers
- Higher conversion on relevant products
- Identify new market opportunities

C
Content Management System - CMS
Content Management System, or CMS, is an application/software that allows you to create or change your website content. These applications are designed so you can create a website without the need for coding and further technical knowledge.
What makes up a CMS
A Content Management System is made up of two main components:
- Content Management Application (CMA) – A front-end, user-friendly interface that allows you to add and modify content on your site.
- Content Management Delivery (CDA) – A back-end, behind the scenes process that takes the content you created or edited, stores it, and makes it visible on your site.
Benefits:
- Easy for inexperienced website creators
- Allows multiple users to log on, create content and edit
- Quick to set up, launch and publish new content
- Pre-set templates/styles give you design options that work
- Many do basic Search Engine Optimisation for you
System Examples:
- Wix
- Squarespace
- WordPress
- Shopify
- Weebly
Conversion Rate Optimisation
Conversion Rate Optimisation, or CRO, is the process of enabling visitors the highest chance of taking action when they visit your website. Your conversion rate is the number of times a visitor completes your goal (Completing a sale, booking an appointment, subscribing to a service etc.)
Knowing What to Optimise
There is no point trying to optimise your site based on guesses or having a sneaky look at your competitors’ website. Knowing what, who for and where to improve is key to CRO success. We can modify your content, layout and calls to action to increase the chances of visitors completing your goal. Methods include:
- Using analytics – looking into where visitors came from, what page they spend most of their time on and lots more.
- Testing – Trying out different things with different visitors.
- Surveys – Placing survey questions on your site or contacting visitors directly for feedback – including those who did and did not convert.
Benefits:
- Better understanding of your target audience and their actions.
- More user-friendly experience.
- Less resources required to focus on lead conversion.
Note: Conversion rate optimisation is about getting more quality from the traffic you already get and then using that data to bring in even more!
Customer Experience
Customer Experience, or CX, is the full experience from every interaction a customer has with your brand. From seeing your advertising to using your website, contacting customer service, the product quality and the delivery process. Naturally, if they like you and how you made them feel, they’ll keep coming back.
The difference between Customer Experience (CX) and User Experience (UX)
Although sounding similar, User Experience is just a small contributing factor to the Customer Experience. User experience measures interaction with one specific product/site and the interaction they had with that. Customer experience measures every interaction a user has with the brand, across multiple channels.
Benefits:
- Increase of revenue as users pay more for superior CX
- Higher awareness of brand on multiple channels
- Increased customer retention
- Organic word of mouth advertising from satisfied customers
How important is Customer Experience for my business?
Mind-blowingly. Here are just 10 facts about CX to convince you.
Customer Journeys
A customer journey is the path your customer takes to get to the destination of completing the purchase of an item/service. Each time the user has any exposure/interaction with your brand, it’s called a touchpoint. The customer journey is mapped out with touchpoints, timings and motivations to help us understand your customers.
Example Touchpoints:
- Social Media Advert
- Google Search for Website
- Website Pop-Up
- Google Review Search
- Customer Service Team Interaction
- Product Delivery
- Follow Up Feedback Surveys
- Post Purchase communications
Benefits:
- Better understanding of your customers
- Higher number of new and returning customers
- Highlights pain points for improvement
Similar Terms:
- Customer Experience
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Mapping
- Journey Mapping
Customer Relationship Management
Customer Relationship Management, or CRM, is software that holds all your customer data. It is your holy grail for improving business partnerships and opportunity tracking – a centralised point of individual customer data. Using the data in a CRM system is an easy way for you to view where the relationship is at and how to move forward to best convert or grow your customer.
CRM software can capture:
- Individual contact details
- Company details
- Company insights/news
- Leads/opportunities
- Reports
- Quoting
- Marketing campaigns
- Call cycle reminders
- Complaint/resolution tracking
- Phone integration
- eCommerce
- Engagement analytics and a whole list more!
Benefits:
- Improved individual customer knowledge and service Improved individual customer knowledge and service
- Ease of tracking and insights into your sales pipeline
- Streamlined communication across your business
- Personalised marketing and interactions
- Save time with everything in one place and automation features
Systems Examples:
- Salesforce
- Insightly
- Pipedrive
- HubSpot
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
Tip: Be relationship-based, not transaction-based.
I
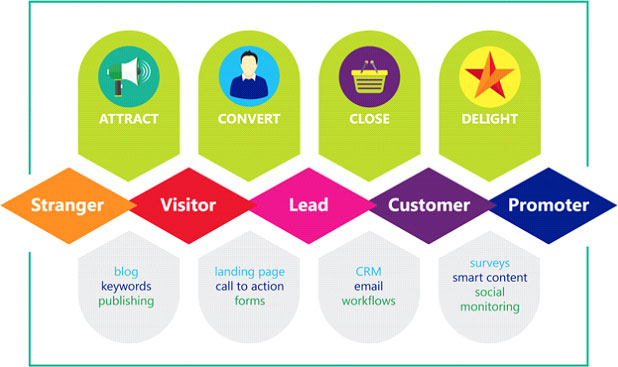
Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing is all about attracting ideal customers to your business, usually finding your business through social media and search engines. Successful inbound marketing is us targeting the right people through the proper channels using quality communications and content to convert and close.
Inbound Marketing vs Outbound Marketing
With inbound marketing, you are drawing people in through quality content in marketing channels you own or have earned spots on. Once potential customers trust the brand, it is only then the process of converting and closing starts. Outbound marketing is pushing your product/service directly out for immediate conversions without the initial warming up step. Outbound marketing is typically paid media advertising.
Benefits:
- High-quality lead generation
- Increased brand awareness
- More cost-effective than traditional outbound marketing
Source: https://blogs.partner.microsoft.com/mpn-unitedkingdom/build-launch-first-inbound-marketing-campaign/
M
Marketing Automation
Marketing Automation is a platform or software that manages the marketing process across different channels, automatically. It can help you take a visitor who entered their data on your website (or other by permission) through a personalised journey.
Essentially it helps you deliver the right content to the right customer at the right time.
Examples of Marketing Automation in use
Lead Conversion –
- A visitor signs up for a freebie online
- Visitor receives a series of emails to build brand awareness/trust.
- When the time is optimal based on the activity from the visitor in response to the emails, a call to action email can be sent.
Sales Order –
- Customer places an order on your website.
- Customer receives automatic, personalised thank you, with confirmation/receipt and tracking details.
- Customer receives follow up survey prompt for business insights.
- Customer later receives relevant upselling or cross-selling emails about related products.
Benefits:
- Develops a personalised relationship with your customer
- Frees up marketing resources
- Increases brand awareness and trust
- Allows for optimal conversion of leads and reduced conversion time
- Provides insights into customer engagement and in-depth data
System Examples:
- MailChimp
- HubSpot
- Marketo
- AutopilotHQ
- ActiveCampaign
- SharpSpring
- Pardot
O
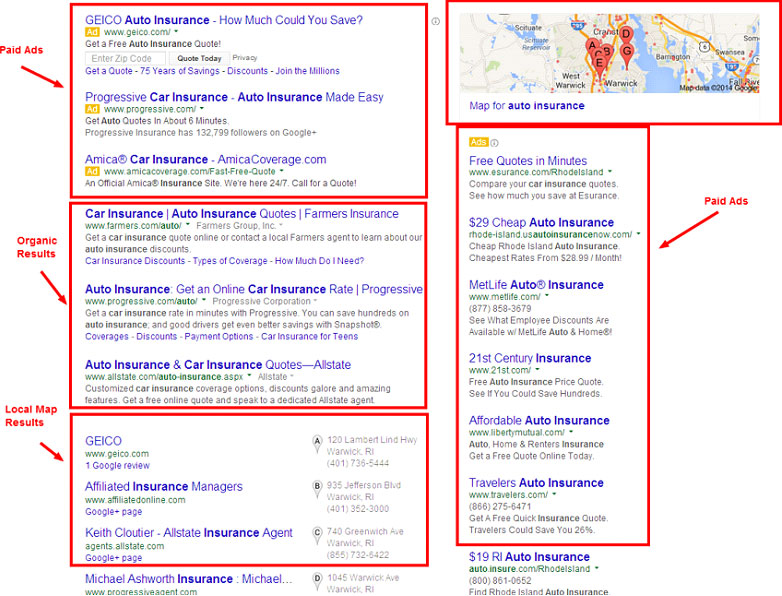
On-page SEO
On-Page Search Engine Optimisation – On-page SEO
On-Page Search Engine Optimisation is the practice of enhancing all the elements of your own website to rank higher on the search engine. This includes everything you have control over such as good technical set up, quality linkable content – written and visual, and how user-friendly your site is.
The difference to Off-page SEO
While On-page SEO contains everything to do with your own website, off-page SEO refers to factors that occur off your website that help determine ranking. Off-page SEO includes links from other sites to your website (backlinks,) how long you’ve had your domain name for and social media interactions.
Benefits:
- Increased traffic to your website
- Better click-through rates from optimised descriptions/titles
- Faster loading page speed
- More user-friendly experience for visitors
Search Engine Results Page Layout:
Source: http://www.insurancemarketinghq.com/2014/03/24/googles-new-search-engine-results-page-layout/
P
Pay Per Click - PPC
Pay Per Click, or PPC, is a type of advertising on the internet (mostly search engines) where you run your ad and pay each time someone clicks on it. One of the most well-known examples of this is Google Ads – the ads that are at the top or side when you Google search. If you have a PPC ad running on Google, linking to your website, each time a user clicks on that ad, and it takes them to your site, you will you pay your set price.
How PPC works
After deciding what your objectives are, choosing spot-on keywords and ensuring your landing page/website has top-notch content, it is time to get your ad underway. Some publishers have a flat rate PPC charge, others run like an auction where you place your ‘per click’ bid price (usually per keyword.) The publisher of which you have chosen (in this example; Google Ads) then takes your bid and ranks your site on quality and relevance to decide where i
